Target Setting
New Product News reports in Forbes magazine that of the 36,000-plus products that will be introduced this year, 80% will fail. While new products and services fail for many reasons (poor quality, excessive cost, late to market, superior competition, etc.), more than half of these failures can be traced directly to an inability to provide better value for the customer.
So how to understand better of voice of customer is very critical for product development and typically is the first step in product planning. At the same time, even many companies spend some sometime to understand the VOC, but they are typically subjective and immeasurable in engineering terminologies. ITI's target setting process combines prioritized customer requirements, customer perceptions and technical competitive benchmarking into specific and measurable performance targets. The results are successful innovative new products, shortened development cycles and a bisis for continuous improvement.
ITI Target Setting Process
Typically requirements research (Voice of the Customer, lessons learned, competitive benchmarking, etc.) is first completed. This information is compiled in the form of customer wants/needs then converted into predictable and measurable targets, typically applying Quality Function Deployment (QFD) methods and tools. Targets must be defined based on the customer-focused product planning and therefore always tie product design decisions to the marketplace, Voice of the Customer (VOC) and business goals.
Targets start at the system level and are cascaded into the subsystems and component over the course of development. Derived from subjective wants and needs of end users and other stakeholders, targets are systematically converted to engineering specifications as measurable and predictable customer-focused targets though QFD and other programs
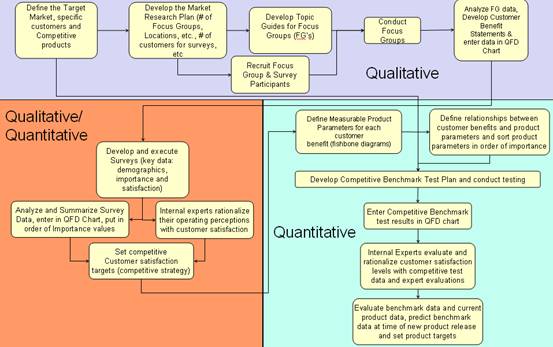
ITI’s target setting process is shown as below. Major steps include:
- Qualitative phase including
- Define target market, target customer and target competitors
- Define number of focus group/locations and customer to be surveyed
- Conduct interview to finalize customer benefits
- Conduct customer clinic as necessary
- Qualitative/Quantitative phase including
- Develop and Conduct survey based on customer benefits and collect data
- Survey satisfaction level for competitors
- Set up targets for new product satisfaction level
- Quantitative phase including
- Convert customer benefits to produce level P/M (Predictable and measurable) targets by using QFD methodology
- Development competitor benchmarking test plan based on P/M targets
- Define final product targets with inputs from experts and measured competitor test data
What we offer
We will work with customer side by side to help customer establish the target setting process, at the same time, transfer the knowhow to customer to really help customer to be successful. During the project, what we offer are as below:
- Capture & analyze Voice of the Customer and Voice of the Business requirements
- Prioritize numerous & diverse requirements
- Turn vague requirements (such as "easy to use") into specific product/service characteristics
- Optimize trade-offs when requirements conflict (such as "light weight yet sturdy")
- Translate requirements into specific, measurable, predictable targets
- Deliver products/services that provide more value to customers
Benefits to Customers
By implementing ITI’s target settings, customer can achieve:
- Better understand customer voice to make sure product is design/made to meet customer requirements and ultimately improve customer satisfaction level
- All customers voice are well captured and finalized before concept design to make sure no rework occurs during design phase
- Provide reasonable targets for concept design to avoid random decision by certain experts
- Help customer establish the target setting process that could be standardized
- Help customer implement QFD methodologies and SFE CONCEPT software as knowledge transfer platform, which can be reused for future design
- Finally reduce the number of prototype and test time and development cost


